
In the digital age, the ability to maneuver through the vast online environment with confidence and security is paramount. This section delves into the critical skills necessary for individuals to safeguard their personal information and make informed decisions in the virtual realm. By equipping oneself with the right knowledge, one can effectively manage their digital footprint and engage with online platforms on their own terms.
The Importance of Acquiring Digital Acumen
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too must our understanding of how to protect our personal data. This involves not only recognizing the potential risks associated with online activities but also knowing how to mitigate these risks. Developing a robust digital acumen empowers individuals to take control of their interactions in the digital world, ensuring that their personal information remains secure and their online experiences remain positive.
Strategies for Enhancing Digital Acumen
To enhance one’s digital acumen, it is essential to stay informed about the latest privacy policies and data protection laws. Additionally, understanding the tools and techniques available for data protection can significantly bolster one’s ability to navigate the digital world safely. This includes learning about encryption methods, secure browsing practices, and the responsible use of social media platforms.
Empowering Consumers Through Data Literacy
In this section, we delve into the complex terrain of digital confidentiality, exploring how individuals can navigate this landscape effectively. The focus is on enhancing personal capability to manage and safeguard one’s information in the digital realm.
Navigating the Digital Privacy Landscape
The digital environment is fraught with challenges related to confidentiality. Each day, countless interactions occur online, from simple browsing to complex financial transactions. Understanding how to maneuver through this space without compromising personal details is crucial. This involves recognizing the various mechanisms through which information is collected, stored, and used by different entities.
One of the primary steps in this navigation is awareness. Users must be cognizant of the types of data that are typically at risk, such as browsing history, purchase records, and even location data. This awareness helps in making informed decisions about which services to use and how to configure privacy settings on various platforms.
Another critical aspect is the evaluation of privacy policies. These documents, often dense and legalistic, outline how a company intends to use the data it collects. While reading and comprehending these policies can be daunting, it is essential for maintaining control over one’s digital footprint. Tools and resources are available to help simplify these documents, making them more accessible to the average user.
Furthermore, engaging with data brokers is a nuanced process. These entities collect and sell data profiles to third parties. Understanding the rights one has when dealing with these brokers, such as the right to access, correct, or delete one’s data, is vital. Strategies for managing these interactions can include opting out of data collection where possible and advocating for more transparent practices.
Lastly, staying informed is an ongoing process. The digital privacy landscape is ever-evolving, with new threats and protections emerging regularly. Resources such as educational websites, forums, and newsletters can provide continuous learning opportunities, helping individuals to stay ahead in the game of digital confidentiality.
In conclusion, navigating the digital privacy landscape requires a blend of awareness, critical evaluation skills, and proactive engagement. By equipping oneself with the necessary knowledge and tools, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to protect their personal information in the digital age.
Navigating the Digital Privacy Landscape
In this section, we delve into the intricate world of information gathering practices prevalent in the digital realm. The focus is on how organizations collect, use, and share personal information, shedding light on the mechanisms behind these processes and their implications for individual privacy.
Overview of Information Collection Practices
Today, numerous entities engage in the systematic collection of personal details. This practice, often driven by commercial interests, involves the gathering of various types of information, from basic identifiers to more sensitive data. The methods employed range from direct interactions, such as filling out online forms, to more covert techniques like tracking online activities through cookies and other digital markers.
Types of Information Gathered
The spectrum of information collected is broad and includes demographic details, browsing history, purchasing behavior, and even location data. Each piece of information contributes to a comprehensive profile that can be used for targeted advertising, personalization of services, or other strategic purposes.
Implications for Privacy
Understanding the extent and nature of information collection is crucial for maintaining control over one’s digital footprint. As data accumulates, so do the potential risks, including breaches of confidentiality and misuse of personal information. Awareness of these practices empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their online interactions and privacy settings.
In conclusion, navigating the digital privacy landscape requires a clear understanding of the mechanisms behind information collection. By recognizing the types of data gathered and the implications of this practice, individuals can better safeguard their privacy and make conscious choices about their digital presence.
Understanding Data Collection Practices
This section delves into the intricate mechanisms by which information is gathered in the digital realm. It aims to shed light on the various methods employed by entities to acquire personal details, emphasizing the importance of awareness in maintaining control over one’s digital footprint.
Data collection practices encompass a wide array of techniques, ranging from straightforward data entry during online transactions to more subtle forms of tracking through cookies and other digital markers. These practices are often integral to the functioning of websites and applications, providing personalized experiences and targeted advertising. However, they also raise significant concerns regarding the extent and purpose of such data gathering.
One common method of data collection is through the use of cookies, which are small text files stored on a user’s device when they visit a website. These cookies can track browsing habits, preferences, and even personal information provided during visits. Another method involves the use of web beacons, also known as clear gifs, which are tiny graphics with a unique identifier, similar in function to cookies, used to track the online movements of web users.
Moreover, many applications and services collect data through user interactions, such as form submissions, search queries, and even the content of messages. This data can be aggregated and analyzed to infer patterns and trends, which can then be used for various purposes, including enhancing service functionality or for more targeted marketing efforts.>
Understanding these practices is crucial for individuals seeking to manage their digital presence effectively. By being aware of how and why data is collected, users can make informed decisions about their online activities and take steps to protect their information from unwarranted access or misuse.
Your Rights Under Data Protection Laws
In this section, we delve into the legal framework that safeguards individual autonomy in the digital realm. It is crucial to comprehend how these regulations function to uphold personal integrity against the backdrop of extensive information gathering.
Overview of Legal Protections
Various statutes and directives worldwide aim to protect personal information. These laws typically grant individuals the authority to control how their details are collected, used, and shared. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe provides a robust set of rights, including the right to access, rectify, and erase personal data.
Key Rights Granted
Under these protections, individuals often have the right to:
- Access: Request and obtain a copy of their personal data held by an organization.
- Rectification: Correct inaccurate personal information and have incomplete data completed.
- Erasure: Request the deletion or removal of personal data when there is no compelling reason for its continued processing.
- Object: Challenge processing based on legitimate interests or the performance of a task in the public interest/exercise of official authority, direct marketing, and processing for purposes of scientific/historical research and statistics.
Exercising Your Rights
To exercise these rights, individuals typically need to contact the data controller directly, often through a designated contact form or email address provided by the organization. It is advisable to keep records of all communications regarding data requests to ensure transparency and accountability.
Challenges and Considerations
While these laws provide a legal basis for asserting control over personal information, challenges such as lack of awareness, complexity in understanding legal terms, and potential resistance from data controllers can hinder the effective exercise of these rights. Therefore, it is essential for individuals to stay informed and proactive in managing their digital footprint.
This understanding not only empowers individuals but also fosters a more transparent and respectful digital environment, where personal autonomy is respected and protected.
Evaluating Online Privacy Policies
In this section, we delve into the critical task of scrutinizing the privacy policies of various online platforms. This process is essential for ensuring that individuals are well-informed about how their personal information is handled by these entities. By carefully examining these documents, users can gain a clearer picture of the extent to which their data is protected and used.
Privacy policies are legal documents that outline the ways in which a company collects, uses, maintains, and discloses information from users. They serve as a crucial tool for transparency, allowing individuals to understand the data practices of the websites and applications they interact with. However, these policies can often be lengthy and complex, making it challenging for the average user to fully comprehend their implications.
To effectively evaluate a privacy policy, one must look for specific elements such as the types of data collected, the purposes for which it is used, and the methods of data sharing with third parties. Additionally, it is important to identify the security measures in place to protect this information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Furthermore, understanding the jurisdiction under which the policy operates can provide insights into the legal protections afforded to users. Different regions have varying regulations regarding data protection, which can significantly influence the rights of individuals.
Lastly, it is advisable to compare privacy policies across similar platforms to discern any significant differences in data handling practices. This comparative analysis can help users make more informed decisions about which services best align with their expectations for data privacy and security.
In conclusion, evaluating online privacy policies is a vital practice that empowers individuals to take control over their personal information. By becoming more adept at reading and interpreting these documents, users can enhance their digital security and make more conscious choices about their online interactions.
Tools and Techniques for Data Security
In this section, we delve into the practical measures individuals can adopt to safeguard their personal information in the digital realm. The focus is on enhancing awareness and implementing strategies that protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and misuse.
Firstly, it is crucial to understand the role of encryption in data security. Encryption tools transform readable data into coded formats that are inaccessible without the correct decryption keys. This technology is pivotal in securing emails, files, and communication channels, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unintelligible to unauthorized parties.
Another essential technique is the use of secure passwords and password managers. These tools help in creating complex, unique passwords for different accounts and https://medium.com/@hago1994/reclaiming-your-privacy-a-comprehensive-guide-to-opting-out-of-whitepages-14c818d1c92d securely store them, eliminating the risk of password reuse and theft. Regular updating of these passwords further enhances security.
Firewalls and antivirus software are also vital components of a robust security strategy. They act as barriers against malicious software and unauthorized access, continuously monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Moreover, two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to a password. This could be a fingerprint, a facial recognition, or a temporary code sent to a mobile device. Implementing 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
Lastly, staying informed about the latest security threats and updates is essential. Regularly updating software and being aware of phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics can help individuals protect their information effectively.
By integrating these tools and techniques into daily digital practices, individuals can significantly enhance their personal security and protect their sensitive information from potential threats.
Engaging with Data Brokers: Rights and Strategies

In this section, we delve into the complex interactions with entities that manage vast amounts of personal information. Here, the focus is on equipping individuals with the knowledge and tactics necessary to assert control over their personal data in dealings with these intermediaries.
Data brokers, entities that collect, analyze, and sell personal information, play a significant role in the modern digital ecosystem. Engaging with these brokers effectively requires a clear understanding of one’s entitlements and the strategic approaches available. Below, we outline key rights and strategies that can be employed to manage interactions with data brokers more proactively.
| Right | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Right to Access | Request a copy of all data held by the broker to understand what information they possess and how it is used. |
| Right to Rectification | Correct inaccuracies or update outdated information to ensure the data is current and accurate. |
| Right to Opt-Out | Utilize the broker’s opt-out mechanisms to prevent the sale or sharing of your data with third parties. |
| Right to Erasure | Request the deletion of personal data under specific circumstances, such as when the data is no longer necessary for the purpose it was collected. |
| Right to Object | Lodge an objection to the processing of personal data, especially in cases where the data is used for direct marketing or profiling. |
Implementing these strategies not only helps in asserting control over personal information but also encourages data brokers to operate more transparently and responsibly. It is crucial for individuals to stay informed and proactive in their approach to data management, ensuring that their interactions with data brokers are both informed and strategic.
Advocating for Stronger Consumer Protections
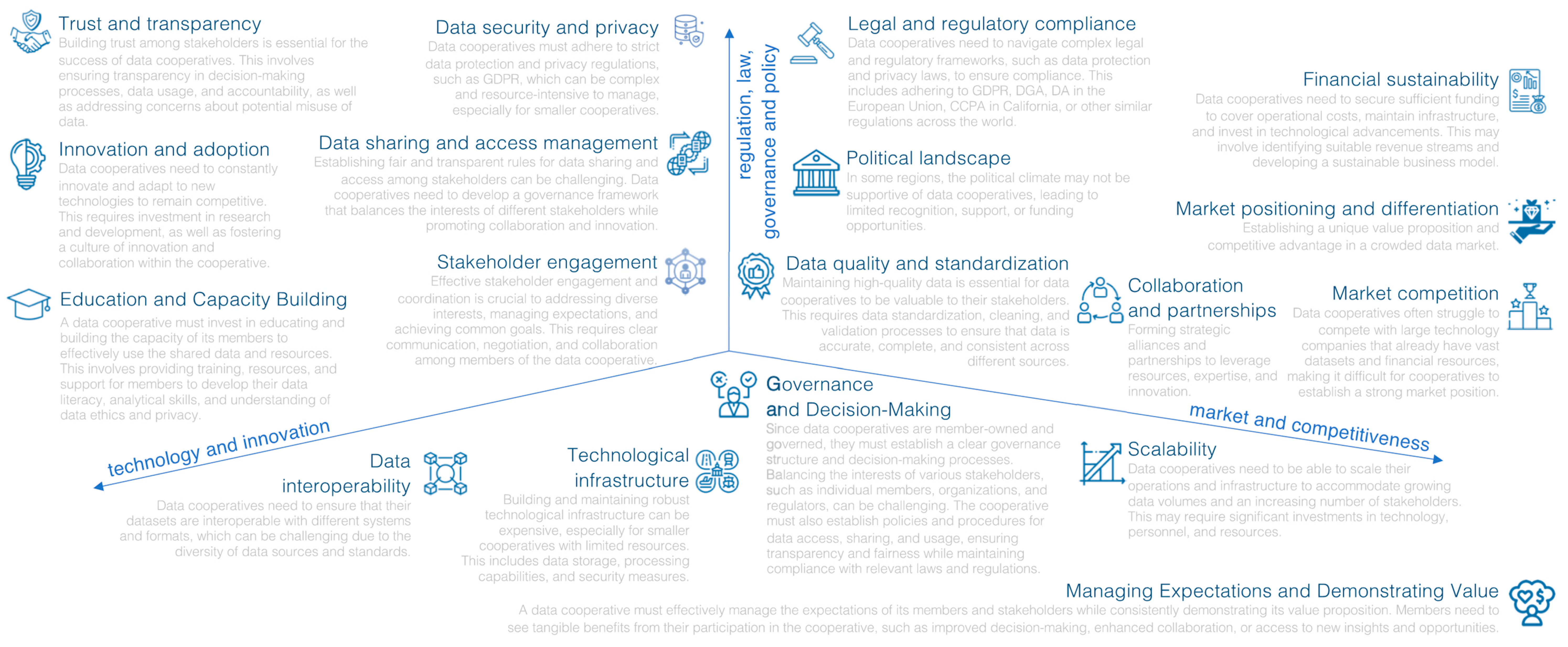
In this section, we delve into the critical role of advocating for enhanced safeguards for individuals in the digital realm. The focus is on promoting robust measures that ensure the protection of personal information and the enforcement of fair practices in the online environment.
To effectively advocate for these protections, it is essential to understand the current landscape of regulations and the gaps that exist. Here are key strategies and considerations:
- Awareness of Existing Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the laws currently in place that govern data protection and consumer rights. This includes understanding the scope and limitations of these laws.
- Engagement with Policy Makers: Actively participate in discussions with legislators and regulators. Provide insights and feedback on proposed changes to laws and regulations.
- Community Education: Educate peers and community members about the importance of consumer protections. This can be done through workshops, seminars, or online forums.
- Collaboration with Advocacy Groups: Join forces with other organizations and groups that share the same goals. Collective action can lead to more significant impacts.
- Utilizing Media: Use various media platforms to raise awareness and influence public opinion. This includes writing articles, participating in interviews, and leveraging social media.
Additionally, it is crucial to stay updated on the latest developments in technology and how they affect consumer protections. This ongoing education is vital for maintaining effective advocacy efforts.
- Continuous Learning: Regularly update your knowledge on emerging technologies and their implications for consumer rights.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish channels through which consumers can report violations or concerns, providing valuable data for advocacy efforts.
- Policy Proposals: Develop and propose new policies or amendments that address current gaps in consumer protections.
By actively engaging in these activities, individuals and groups can play a pivotal role in shaping stronger protections for all in the digital age.
Staying Informed: Resources for Continuous Learning

In this section, we delve into the importance of maintaining an ongoing education regarding personal information management and digital security. The ever-evolving nature of technology necessitates a proactive approach to learning and adapting to new developments in this field.
To effectively safeguard one’s digital presence, it is crucial to access reliable sources of information that provide updates on the latest trends, regulations, and tools related to digital security. This includes staying abreast of changes in legislation that affect how personal information is collected, stored, and used by various entities.
One valuable resource is government websites, which often publish guidelines and updates on privacy laws and consumer protections. Additionally, non-profit organizations dedicated to digital rights frequently offer comprehensive guides and webinars that can enhance one’s knowledge and skills in managing personal data.
For those interested in a more hands-on approach, online courses and workshops are available that cover a range of topics from basic cybersecurity practices to advanced techniques in data encryption. These educational platforms not only provide theoretical knowledge but also practical exercises that help in applying these concepts in real-world scenarios.
Moreover, engaging with communities and forums focused on digital security can be immensely beneficial. These platforms allow for the exchange of ideas and experiences, providing a rich environment for learning from others’ successes and challenges in managing their digital footprint.
In conclusion, keeping oneself informed is a dynamic process that requires consistent effort and engagement with various educational resources. By doing so, individuals can better equip themselves to navigate the complexities of the digital world and protect their personal information effectively.